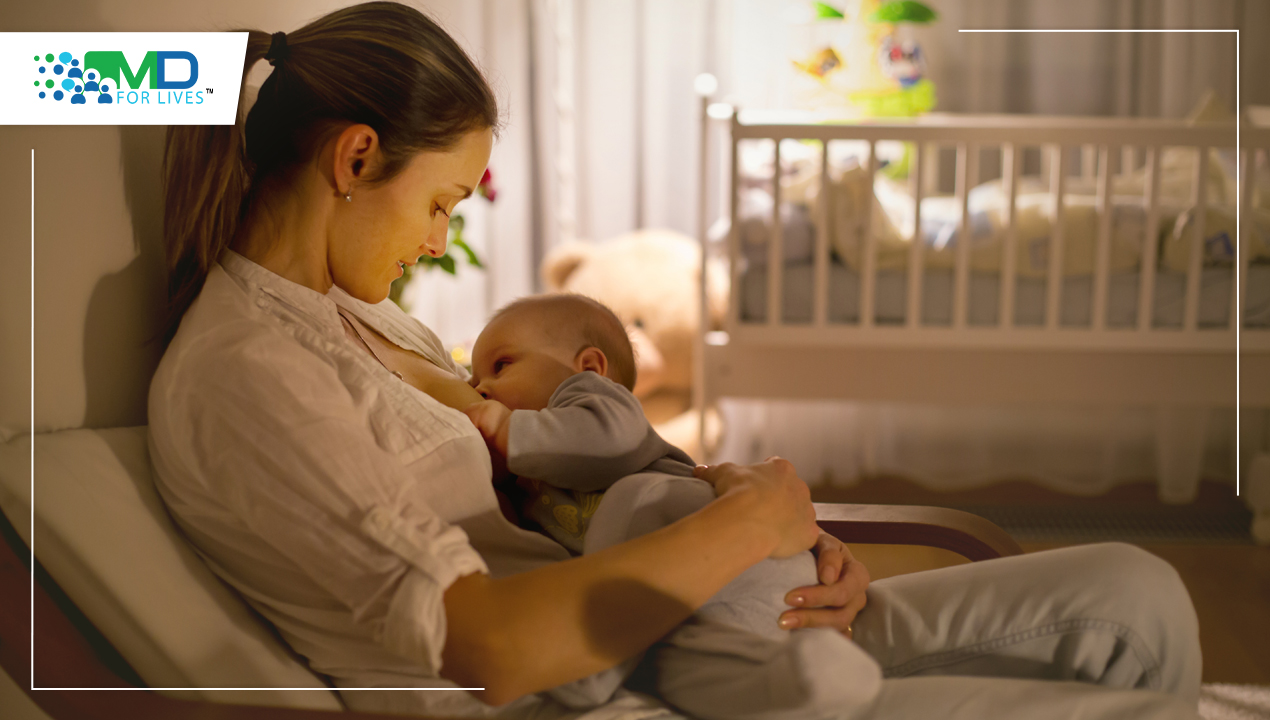
One of the best ways to ensure a child’s health and survival is to breastfeed them. However, the rate of infants who do not receive breast milk exclusively for the advised six months is close to two out of every three, and it has not decreased over the past twenty years.
To promote healthy growth, the milk changes in volume and composition depending on the time of day, frequency of nursing, and age of the baby. Breast milk is the ideal food for your child.
Benefits of Breastfeeding:
The benefits of breastfeeding include the following:
- Breast milk is the best food for babies. It is secure, hygienic, and rich in antibodies that help shield kids from many common illnesses.
- Breast milk continues to supply up to half or more of a child’s nutritional needs during the second half of the first year of life and up to one-third of a child’s nutritional needs during the second year of life, in addition to all the energy and nutrients that an infant needs during the first few months of life.
- Breastfed children outperform non-breastfed children on intelligence tests, are less likely to be overweight or obese, and are less likely to develop diabetes later in life.
- Ear infections and stomach bugs are also less common in breastfed babies.1
- Breast-feeding preterm babies has been linked to a lower incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis.
- Breastfeeding can protect against a variety of acute respiratory and gastrointestinal illnesses.
- It is associated with a lower risk of developing eczema, atopic dermatitis, and asthma.
- Breastfed infants may have a lower risk of developing ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
There is evidence that breastfeeding lowers the risk of childhood leukemia.

Why breastfeeding is important?
“Breastfeeding provides unmatched health benefits for babies and mothers. It is the clinical gold standard for infant feeding and nutrition, with breast milk uniquely tailored to meet the health needs of a growing baby. We must do more to create supportive and safe environments for mothers who choose to breastfeed.”
Dr. Ruth Petersen, director of CDC’s Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity
Breastfeeding is beneficial to both the baby’s and the mother’s health. It is also beneficial to your family and society. Your baby can feel, smell, and see you when you hold him or her close during breastfeeding. This assists you in developing a close, loving bond with your baby. Breastfeeding can take some time for some moms getting used to. It might even be difficult at first. However, the value to you and your child is worth it. Breastfeeding can be started and maintained with the assistance of family and friends.
- Breast milk is always readily available, fresh, clean, and safe.
- It saves time because you don’t have to mix formula or clean bottles.
- It is always prepared for your child.
- It produces no waste and is environmentally friendly.
- Breast milk is free of charge. Less illness means lower healthcare costs.
Benefits of breastfeeding for the mother
- Promotes faster postpartum weight loss by burning 500 extra calories per day to build and maintain a milk supply.
- The uterus is stimulated to contract and return to normal size.
- There is less postpartum bleeding.
- Two naturally calming hormones produced by breastfeeding, oxytocin and prolactin, aid nursing mothers in feeling less anxious and happier.
- It increases self-esteem and assurance.
- Overall, breastfed babies cry less and experience fewer childhood illnesses. For the entire family, breastfeeding can support physical, mental, and spiritual wellness.
- Travel is made simpler when nursing. The temperature and cleanliness of breast milk never change.
- Physical and emotional bonding between a mother and child is boosted. Breastfeeding encourages more holding, stroking, and skin-to-skin contact. Many people believe that nurturing relationships during the first few years of life helps children and adults with social and behavioral issues.
- Babies who are breastfed learn to trust their caregivers and their mothers learn to read their baby’s cues. The infant’s early behavior is influenced by this.
What does new breastfeeding research reveal?
According to a recent study, breastfed women were less likely than non-breastfed women to develop heart disease, have a stroke, or die from cardiovascular disease.
- The majority of the women, 82%, revealed that they had breastfed their children at some point.
- Women who reported breastfeeding throughout their lifetime had an 11% lower risk of developing cardiovascular disease compared to women who never breastfed.
- Women who breastfed at least once during their lives were 14% less likely to develop coronary heart disease, 12% less likely to experience strokes, and 17% less likely to pass away from cardiovascular disease over the course of an average follow-up of 10 years.
- Compared to women who did not breastfeed, those who did so for at least 12 months throughout their lifetimes appeared to have a lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Women of different ages or according to the number of pregnancies did not have significantly different risks for cardiovascular disease.

The positive effects of breastfeeding on mothers must be effectively communicated, breastfeeding recommendations must be raised in awareness, and interventions to promote and facilitate breastfeeding must be implemented and reinforced.

MDForLives is a global healthcare intelligence platform where real-world perspectives are transformed into validated insights. We bring together diverse healthcare experiences to discover, share, and shape the future of healthcare through data-backed understanding.