According to the most recent findings from the MONARCH 3 study, combining Verzenio with an aromatase inhibitor improves overall survival by 12.6 months in advanced-stage, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer.
The majority of breast lumps are not cancerous (malignant). Non-cancerous breast tumors are abnormal growths that do not spread beyond the breast. Although not life threatening, some benign breast lumps can increase a woman’s risk of developing breast cancer. Any breast lump or change should be evaluated by a medical professional.
Breast Cancer Symptoms and Signs
- Breast tissues that feel thicker or lumpier than the rest of the breast
- A breast’s size, shape, or appearance changing
- Alterations to the breast’s skin, such as dimpling
- A recently flipped nipple
- The pigmented area of skin around the nipple (areola) or breast skin peels, scales, crusts, or flakes.
- Over the breast, there may be redness or pitting similar to that of an orange.
What is Inflammatory Breast Cancer?
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and deadly disease in which cancer cells block lymph vessels in the breast skin. This type of breast cancer is referred to as “inflammatory” because the breast frequently appears swollen and red or inflamed. The majority of inflammatory breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas, which means they began in the milk ducts of the breast and spread beyond them.
Inflammatory breast cancer is more commonly diagnosed in younger women. Inflammatory breast tumors are frequently hormone receptor negative, which means they cannot be treated with hormone therapies that inhibit the growth of cancer cells fueled by estrogen, such as tamoxifen. Obese women are more likely than normal-weight women to develop inflammatory breast cancer.
Breasts that are at least one-third swollen and red (erythematous) are signs of inflammatory breast cancer. Additionally, the breast’s skin can look pink, reddish-purple, or bruised. The skin may also have ridges or appear pitted, similar to orange skin (also known as peau d’orange). The accumulation of fluid (lymph) under the breast skin is what causes these symptoms. This fluid accumulation happens as a result of cancer cells obstructing lymphatic vessels in the skin, which stop lymph from flowing normally through the tissue. Occasionally, a solid tumor in the breast may be felt during a physical examination, but most of the time, a tumor cannot be felt.
It can be challenging to diagnose breast cancer that is inflammatory. Frequently, a screening mammogram or a physical examination will not reveal any lumps. Additionally, the dense breast tissue that most women with inflammatory breast cancer have makes it more challenging to detect the disease during a screening mammogram. Furthermore, due to its aggressive nature, inflammatory breast cancer can develop between routine screening mammograms and advance rapidly.
It is typically treated with radiation therapy after surgery to remove the tumor and systemic chemotherapy to help shrink the tumor. A multimodal approach to treatment is what it is known as. According to studies, women with inflammatory breast cancer who receive multimodal treatment respond better to treatment and live longer.
Many patients with inflammatory breast cancer have the option to take part in clinical trials, and all patients with this condition are urged to think about receiving treatment in a clinical trial.
Verzenio Plus Aromatase Inhibitor in Improving Survival in Advanced-Stage, Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer
The MONARCH 3 study included 493 postmenopausal women with advanced-stage, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. None of the women had received advanced-stage disease hormonal therapy.
According to the latest results from the MONARCH 3 study, combining the targeted therapy Verzenio with an aromatase inhibitor as the first treatment for advanced-stage, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer improved overall survival versus using an aromatase inhibitor alone.
Verzenio is a CDK4/6 (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor. A kinase is a type of protein found in the body that aids in the control of cell division. Verzenio works by inhibiting cancer cell division and growth.
The women were randomly assigned to one of two treatment groups by the researchers:
- Verzenio was given to 328 women along with one of two aromatase inhibitors: Arimidex or Femara
- 165 women were given either Arimidex or Femara along with a placebo pill, which contained no medicine but looked identical to Verzenio.
Verzenio plus an aromatase inhibitor improved progression-free survival by about 14 months, according to MONARCH 3 results published in 2019. The length of time a person lives without cancer progressing is referred to as progression-free survival.
After about 5.8 years of follow-up, the difference of 12.6 months was not statistically significant in this latest analysis. The findings were trending toward statistical significance, and a longer follow-up period would almost certainly show significance. When the researchers focused on women with visceral disease — that is, breast cancer that had spread to soft internal organs such as the liver or lungs — Verzenio was found to improve overall survival by 16.3 months.
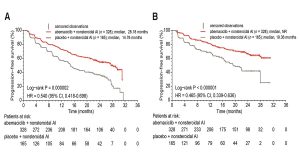
Source: MONARCH 3 final PFS: a randomized study of abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast cancer (Figure 1)
Among women with visceral disease, overall survival was:
- For females taking Verzenio and an aromatase inhibitor, 65.1 months
- For females taking an aromatase inhibitor alone, 48.8 months.
This result demonstrates unequivocally that Verzenio increases overall survival when combined with an aromatase inhibitor.

MDForLives is a global healthcare intelligence platform where real-world perspectives are transformed into validated insights. We bring together diverse healthcare experiences to discover, share, and shape the future of healthcare through data-backed understanding.






