While medical breakthroughs often capture headlines, a quieter threat is steadily advancing – Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). This growing crisis has the potential to reverse decades of medical progress and undermine our ability to treat even the most common infections. Antimicrobial resistance is no longer a distant concern. It is a present-day challenge that’s already affecting healthcare systems worldwide. As resistance grows, routine treatments become less effective, post-surgical complications increase, and once-manageable infections become harder to control.
The overuse and misuse of antibiotics have significantly accelerated this issue. But addressing AMR goes beyond reducing prescriptions. Addressing this crisis calls for shared responsibility, informed choices, and coordinated action at every level of the healthcare system.
Antimicrobial Resistance: What Gave Rise to this Phenomenon?
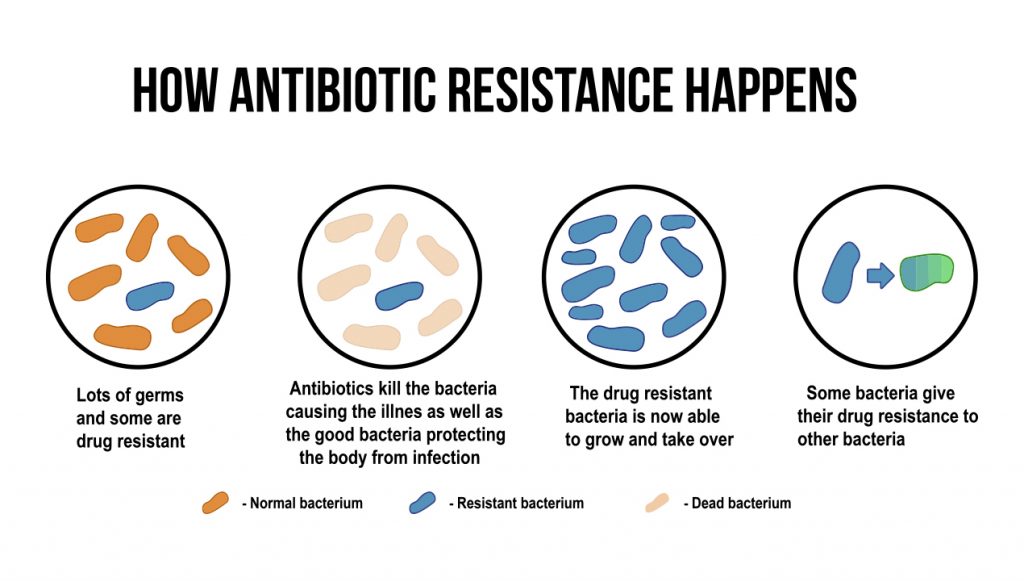
Antibiotics, those marvels of modern medicine, have stood as formidable guardians, rescuing countless lives from the clutches of bacterial infections. These pharmaceutical wonders revolutionized healthcare, turning once life-threatening diseases into manageable conditions. Yet, the very tools that have been our allies in the war against infections are now facing a formidable adversary – antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
The rise of antimicrobial or antibiotic resistance is a tale of unintended consequences; a consequence of our own success. As these powerful drugs became more widely available, their overuse and misuse inadvertently fueled the evolution of bacteria, pushing them to adapt and survive in the face of antibiotic onslaughts.
However, over time, some resilient foes began to adapt, developing strategies to withstand the onslaught and rendering these once-mighty drugs ineffective. This phenomenon is not a mere glitch in the system; it’s a biological chess match where bacteria, in their quest for survival, outmaneuver our medical advancements.
What is Antibiotic Resistance?
Antibiotic resistance occurs through various mechanisms including – genetic mutations and the exchange of genetic material between bacteria. This adaptability is a fundamental characteristic of bacteria, allowing them to survive and thrive in diverse environments. Unfortunately, it’s this very adaptability that poses a significant challenge to our ability to treat bacterial infections effectively.
The Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistance
The implications of antimicrobial/antibiotic resistance are far-reaching. Simple infections that were once easily treatable may now become life-threatening. Medical procedures such as surgeries, chemotherapy and organ transplants, which rely heavily on the effectiveness of antibiotics to prevent and treat infections, are at risk of becoming riskier endeavors.
As per findings disclosed in The Lancet, the toll of antimicrobial resistance on a global scale is grim, with the loss of 1.27 million lives documented and a disconcerting correlation to nearly 5 million deaths in the year 2019 alone. Within the United States, the gravity of the situation is evident, with over 2.8 million cases of antimicrobial-resistant infections documented annually. The dire consequence of this resistance is witnessed by the loss of more than 35,000 lives each year, as reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in their 2019 Antibiotic Resistance (AR) Threats Report.
Things get scarier when we talk about a bacterium called Clostridioides difficile. It’s not usually resistant to antibiotics, but it causes severe diarrhea and is linked to using antibiotics. When you add this bacterium to the numbers, the situation in the U.S. becomes even worse, with over 3 million infections and a shocking 48,000 deaths, showing how dangerous antibiotic resistance can be.
Insight from the WHO: The World Health Organization (WHO) warns that antibiotic resistance could lead to a future where common infections, injuries and minor surgeries may become deadly due to the inability to treat them effectively. This could result in increased higher medical costs, prolonged hospital stays, and higher mortality rates, significantly straining healthcare systems globally.
Causes of Antimicrobial Resistance
The surge in antibiotic resistance is not a single-dimensional challenge but rather a complex interplay of various factors. Understanding these contributing elements is crucial for devising effective strategies to mitigate the growing threat.
Here are some key factors that contribute to the causes of antimicrobial resistance:
- Over-Prescription of Antibiotics: Healthcare professionals sometimes prescribe antibiotics even when they might not be necessary. This over-reliance on antibiotics, often driven by a desire to quickly alleviate symptoms, can contribute to the development of resistance. Patients may receive antibiotics for viral infections, against which antibiotics are ineffective, inadvertently fostering an environment where bacteria can evolve and adapt.
- Use of Antibiotics in Agriculture: Antibiotics are extensively used in agriculture for various purposes, such as promoting animal growth and preventing disease in livestock. The widespread use of antibiotics in this sector contributes to the emergence of resistant strains of bacteria. These resistant bacteria can then find their way into the food chain, posing a risk to human health.
Noteworthy Fact: Around the world, about two-thirds (66%) of antibiotics are given to farm animals instead of people. Most of the time, these antibiotics are used regularly to keep animals like pigs, poultry, and sometimes cows in cramped and unsanitary conditions, where diseases spread easily. - Incomplete Antibiotic Courses: Patients not completing the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by healthcare providers is a common yet significant factor. Incomplete courses can leave behind bacteria that may have developed some level of resistance during the initial stages of treatment. These surviving bacteria can then proliferate and spread, potentially leading to more resistant strains.
- Availability of Antibiotics Without Prescription: In some regions, antibiotics are available without a prescription, allowing individuals to self-diagnose and self-medicate. This unrestricted access can lead to inappropriate use, including the use of leftover antibiotics from previous prescriptions. This antibiotic exposure contributes to the development of resistance and makes it challenging to regulate their proper administration.
Together, We Can Overcome Antimicrobial Resistance!
Finally, it’s time to share some good news on world antimicrobial awareness week 2023 – governments, healthcare professionals and international organizations are working together to address antimicrobial resistance. Efforts underway involve the development of new antibiotics or viruses to outsmart antibiotic-resistant bacteria, advocating for responsible use of current antibiotics, and educating healthcare providers and the public about the critical importance of using antibiotics wisely.
Individuals too can contribute to the fight against antibiotic resistance by using antibiotics only when prescribed by a qualified healthcare professional, completing the full prescribed course and never sharing or using leftover antibiotics. Additionally, practicing good hygiene such as regular handwashing, can help prevent the spread of infections, reducing the need for antibiotic treatment.
Physicians who want to become an integral part of the evolving healthcare landscape through MDForLives, participate in our paid medical surveys! Your unique insights carry the potential to mold the development of groundbreaking products and treatments, steering the course of healthcare advancement. In addition to survey participation, you are encouraged to contribute your expertise in our discussion forums or share your knowledge through blogs and case studies.

MDForLives is a global healthcare intelligence platform where real-world perspectives are transformed into validated insights. We bring together diverse healthcare experiences to discover, share, and shape the future of healthcare through data-backed understanding.








