Since blood transfusion was first introduced in the 17th century, there have been umpteen efforts to push its boundaries, enabling healthcare professionals to save countless lives. Whether in surgeries, trauma care, cancer treatment, or the management of chronic conditions, advancements in blood transfusion technology have enabled the healthcare industry to unlock the full potential of contributions made by blood donors. Let’s discuss some of the innovations in blood collection and storage that are expanding the possibilities of blood transfusion while improving the outcomes for both donors and patients who benefit from the donated blood.
Blood Donation and Collection – New Milestones
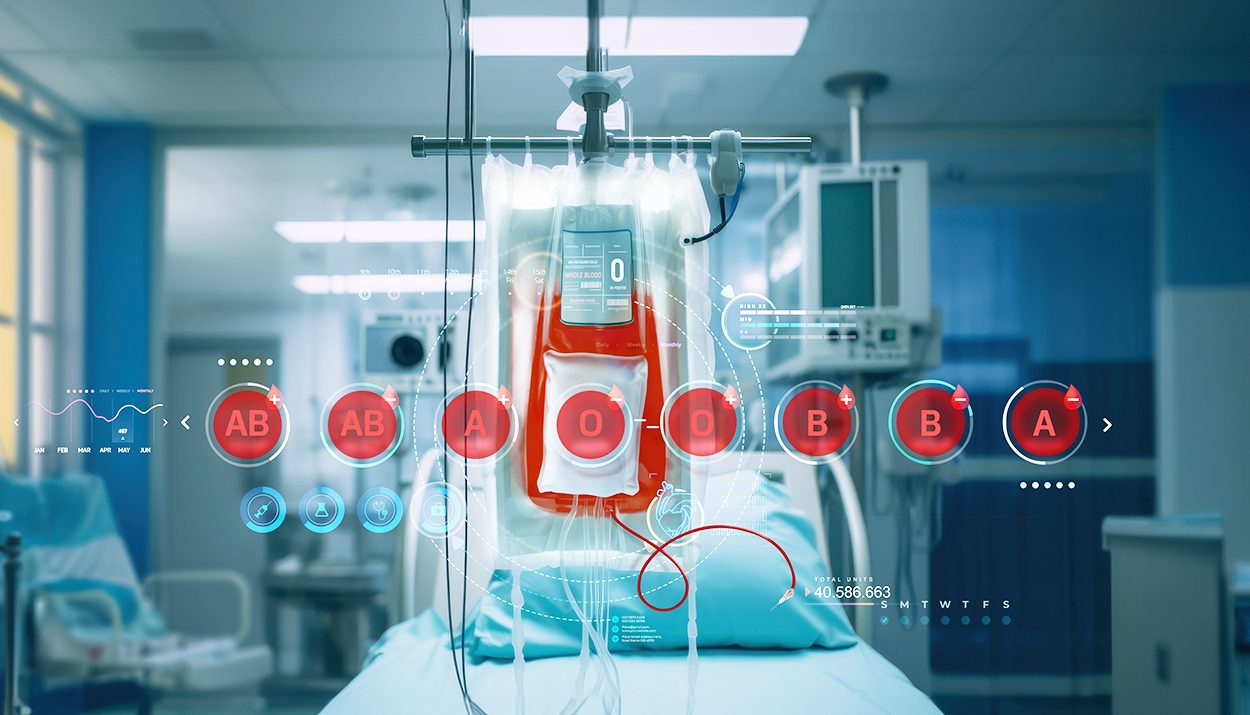
Breakthroughs in blood collection technology are augmenting the efficiency and safety of the donation process while enhancing donor experience. One significant advancement is automated apheresis, a technique that enables the collection of specific blood components such as platelets, plasma, or red blood cells.
Automated apheresis machines separate blood components during donation, returning unused components to the donor’s bloodstream while collecting the needed components. This process ensures higher yields of specific blood products and shortens the overall donation time, typically taking 1 to 2 hours, depending on the collected component. For instance, platelet donations via apheresis can yield enough platelets from a single donation that would otherwise require multiple whole blood donations.
Combined with mobile donation units, this technology marks a great leap forward for blood transfusion technology. They bring donation opportunities directly to communities, workplaces, and events, making donating more convenient for individuals. Technological solutions, such as online scheduling platforms and donor management systems, streamline the donation process and provide donors with real-time information on donation opportunities and their impact. Even after the blood is collected, safe and efficient logistics and storage are implemented to maximize the impact made by the blood donors.
Enhancing Safety in Blood Transfusion Technology with Pathogen Reduction Technologies (PRT)
PRT marks a revolutionary step forward in blood transfusion. It uses photochemical treatments and UV light to effectively target various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites, rendering them inactive in donated blood. This is vital for individuals with weakened immune systems, such as cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy or those receiving organ transplants, who are especially vulnerable to infections. Implementing PRT significantly lowers the risk of transfusion-transmitted infections (TTIs) during medical procedures and emergencies, where rapid and safe access to blood can be a matter of life or death.
Despite its undeniable benefits, adopting PRT comes with challenges that need careful consideration. These include managing the initial costs of technology implementation, integrating new procedures into existing blood collection and distribution systems, and navigating the regulatory landscape that varies across different regions and countries.
Nevertheless, PRT’s advantages in maintaining a secure and sustainable blood supply are profound. It ensures that donated blood meets stringent safety standards, safeguarding recipients’ health and well-being. Moreover, by reducing the incidence of TTIs, healthcare providers can minimize the burden on healthcare systems and improve patient outcomes.
Advanced Blood Storage Solutions – Improving Longevity of Donated Blood

Traditional blood storage methods have faced numerous challenges, such as limited shelf life and quality degradation. Innovations in storage techniques have addressed these issues, enhancing the viability and longevity of donated blood.
Let’s explore some of these breakthroughs in blood storage solutions:
Cryopreservation Of Red Blood Cells
Traditional storage of red blood cells (RBCs) at 4°C limits their shelf life to about 42 days. Cryopreservation, by freezing RBCs below -80°C, extends their shelf life to ten years by halting deterioration. This is especially valuable for rare blood types and emergencies requiring diverse blood supplies.
Additive Solutions for Enhanced Preservation
Researchers have developed advanced additive solutions to improve blood storage conditions. These solutions, containing nutrients and stabilizers, preserve the viability and functionality of RBCs, platelets, and other blood products by mitigating temperature and oxidative damage. This advancement prolongs shelf life and ensures therapeutic efficacy upon transfusion.
Platelet Storage with Cold Temperature Methods
Platelets, essential for clotting and wound healing, are traditionally stored at 20-24°C with agitation, limiting their shelf life to 5-7 days. Recent advancements in cold storage (1-6°C) extend platelet shelf life by slowing metabolic degradation. This innovation is especially beneficial in areas with limited donors or high demand.
These blood storage solutions represent significant strides in blood banking and transfusion medicine. Ongoing research aims to refine these techniques further, ensuring stored blood components meet stringent quality standards and remain viable for longer periods. Enhanced blood storage solutions are crucial for supporting healthcare systems worldwide, particularly in emergency medicine, surgery, and treatments for chronic diseases. By leveraging these advancements, healthcare providers can better manage blood supplies, reduce wastage, and improve patient outcomes through timely and effective transfusions.
Future Directions in Blood Transfusion Technology
The future of blood transfusion technology is promising, with emerging trends poised for further advancements. Collaborative research among scientists, clinicians, and industry leaders will drive these improvements, ensuring the advancements in blood transfusion meet growing patient needs. These innovations, from pathogen reduction technologies to personalized transfusion strategies boost the safety, efficacy, and accessibility of blood transfusions, ultimately saving lives.
This World Blood Donor Day, let’s recognize the critical role of ongoing research and innovation in transfusion and honor the blood donors who make it all possible. Healthcare professionals interested in contributing to advancements in healthcare can join MDForLives. The platform offers opportunities to participate in paid medical surveys aligned with your expertise.
Share your insights, case studies, and articles at collaboration@mdforlives.com to contribute to the dialogue on blood donation and earn exclusive rewards!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is blood transfusion technology?
Blood transfusion technology is the collection, testing, processing, storage, and safe transfusion of blood and blood components to patients who need them. It ensures that donated blood is compatible, free from infections, and handled according to strict medical standards.
2. What are the three types of Blood transfusions?
The three main types of blood transfusions are red blood cell transfusions, platelet transfusions, and plasma (or fresh frozen plasma) transfusions. Each type serves a different purpose, such as treating anemia, aiding blood clotting, or restoring blood volume and essential proteins.
3. What are the 5 components of a blood transfusion?
A. Royden D’Souza is a professional writer with over 5 years of experience in the healthcare industry. He holds an engineering degree and has worked with several brands to meet their content requirements. He is passionate about writing engaging content for healthcare professionals, allied healthcare professionals, and nurses.