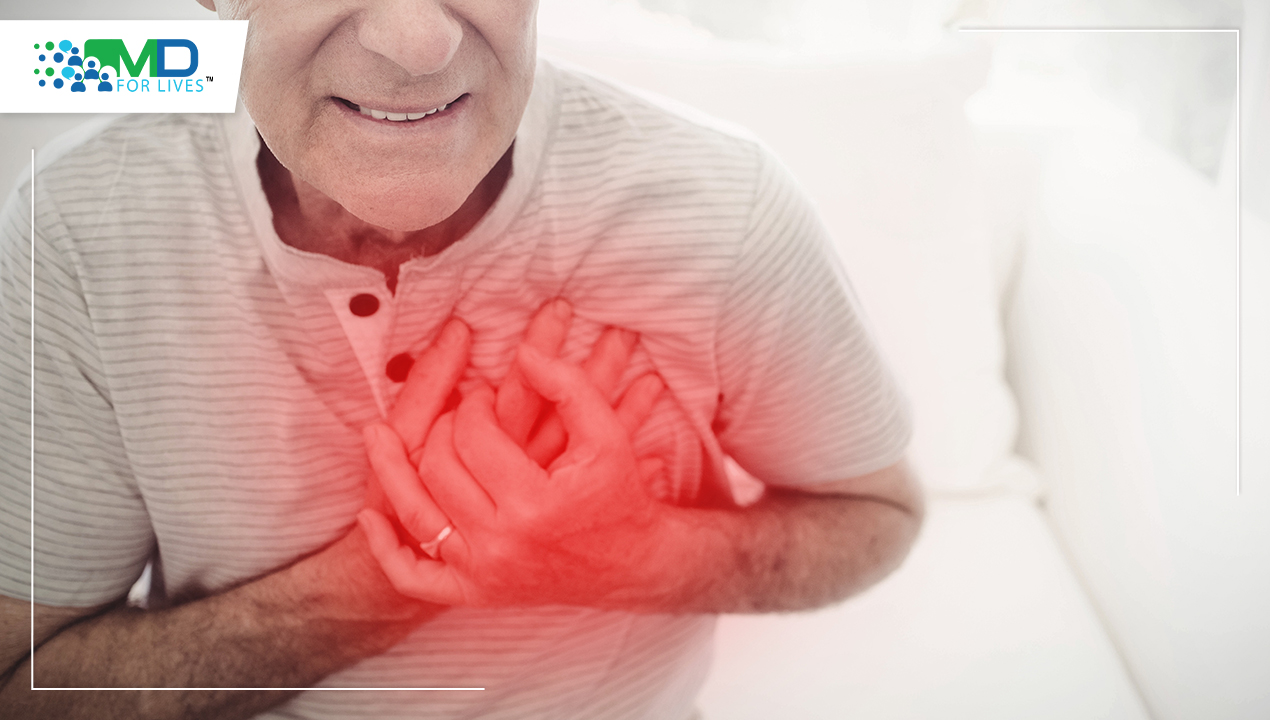
In today’s fast-paced world, where people are busy earning their bread and butter and often struggle to maintain healthy habits like regular exercise and a balanced diet, it’s unsurprising that health complications are on the rise. Among these rising health concerns, cardiac problems, more specifically – cardiac arrests, have gained significant prominence. This medical emergency strikes fear in the hearts of both – a patient with cardiac arrest and healthcare professionals. Cardiac arrest represents the sudden cessation of the heart’s pumping function and it’s a life-threatening event that necessitates immediate intervention to resuscitate the patient. While modern medicine has made considerable advancements in improving survival rates, recent research has shed new light on the experiences of patients, who undergo this distressing ordeal.
In this blog, we will talk in-depth about the world of NDEs (near to death experiences) and the groundbreaking research that suggests patients may recall these experiences after cardiac arrest. We will explore the nature of NDEs, the scientific skepticism surrounding them and the latest findings that have reignited interest and debate in the medical and scientific communities. Furthermore, we delve into – what conditions cause cardiac arrest and how to prevent it.
How Does NDEs Feel Like to a Patient with Cardiac Arrest?

NDEs are defined as profound psychological events typically occurring when a person is close to death or in a state of clinical death. A patient with heart attack and who has experienced NDEs will usually recall dreamlike sensations such as – being pursued by the police or caught in the rain, others experienced more positive recollections. These included witnessing a light, traversing a tunnel, encountering a family member or feeling powerful emotions like love, serenity and profound peace.
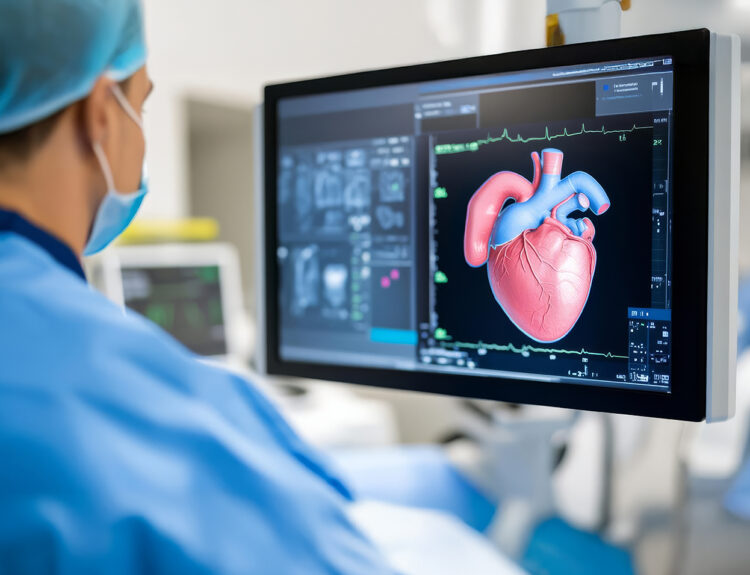
In fact, in a unique study published in the journal Resuscitation, Dr. Parnia and colleagues in the US and the UK observed 567 people who had cardiac arrests in 25 hospitals. Sadly, fewer than 10% survived because cardiac arrests are often fatal, even with doctors present to provide CPR. The researchers managed to interview 28 of the 53 survivors out of which, 11 of them said that they had memories or perceptions hinting at some awareness during their resuscitation. The researchers also checked brain oxygen and electrical activity in some patients and discovered various types of waves (gamma, delta, theta, alpha and beta) indicating signs of mental function during the CPR session.
Cardiologists or Psychiatrists – Who are more interested in NDEs?
Well, the topic itself is very interesting hence, both cardiologists and psychiatrists are interested to learn more about NDEs. But, to pick any one of them, it’s definitely the psychiatrists who are still trying to delve deeper into the crux of how a patient with heart attack might or has experienced death while they are almost struggling to live.

Even before the term “near-death experience” (NDE) became widely known through Raymond Moody’s book – “Life after Life,” there were psychiatrists like Russell Noyes who wrote about it in journal articles. Elisabeth Kubler-Ross, known for her work on death and dying, also had a keen interest in NDEs. More recently, psychiatrist Bruce Greyson has been a prominent figure in NDE research and served as the editor of the Journal of Near-Death Studies for many years. Contemporary psychiatrist Glen Gabbard has also explored various aspects of this phenomenon as well.
Beyond psychiatry, professionals from diverse fields, including doctors, psychologists, nurses, social workers and chaplains, have delved into NDE research, contributing their unique perspectives to this captivating subject. It’s no surprise that a wide range of experts find NDEs fascinating and worth studying.
What conditions cause cardiac arrest?
After talking you all through the interesting facets of NDEs, it’s time to get serious and talk about cardiac arrest. According to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, every year over 356,000 individuals in the United States experience out-of-hospital cardiac arrests and sadly, between 60% and 80% of them do not survive until they reach the hospital. Therefore, it’s evident how serious this health issue is.
Now, let’s straight away get into the pointers where we can discuss what causes cardiac arrest:
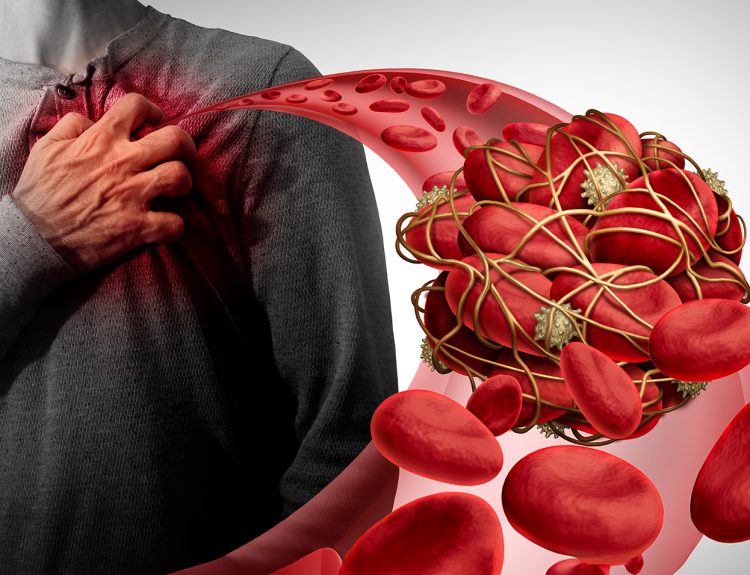
- Scarring of Heart Tissues: When the heart’s tissue is scarred, which can happen after a heart attack or due to other reasons, it becomes more vulnerable to dangerous ventricular arrhythmias. The initial six months following a heart attack pose a particularly high risk for sudden cardiac arrest in patients with atherosclerotic heart disease.
- Thickened Heart Muscles: When the heart muscle thickens, known as cardiomyopathy, it can be due to factors like high blood pressure, heart valve issues or other causes. A heart muscle that’s in poor health increases the risk of a patient with cardiac arrest.
- Heart Medications: Some of the medicines can trigger arrhythmias leading to sudden cardiac arrest. This includes the paradoxical effect where antiarrhythmic drugs designed to treat arrhythmias can sometimes induce ventricular arrhythmias even at regular doses, known as the ‘Proarrhythmic Effect’. Notably, significant alterations in blood levels of potassium and magnesium, often due to diuretic use, can also result in life-threatening arrhythmias and cardiac arrest.
- Blood Vessels Abnormalities: Abnormalities in blood vessels, which are infrequent and typically affect the coronary arteries and aorta, can be a concern. When these abnormalities are present, the release of adrenaline during strenuous physical activity may provoke sudden cardiac arrest.
- Electrical Abnormalities: Irregularities in the heart’s electrical system, such as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and Long QT syndrome, have the potential to trigger sudden cardiac arrest, particularly in children and young individuals.
Please note: Cardiac arrest can occur in healthy people too due to recreational drug usage.
Cardiac Arrest Treatment: Here’s What the Physicians Do to Save Lives
Effective treatment for sudden cardiac death involves a range of interventions such as:
- CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation): Immediate administration of CPR is critical when addressing sudden cardiac arrest to restore blood circulation and prevent potential fatalities.
- Heart Rhythm Restoration (Defibrillation): Defibrillation, the process of resetting the heart’s rhythm, is crucial. It can be accomplished using an automated external defibrillator (AED), often available in public locations for swift action.
- Medications: Healthcare professionals may administer medications to manage a patient with chest pain, irregular heartbeats and other symptoms that indicate heart attack.
- Heart Surgery: In some cases, patients may require heart procedures or surgery to implant specialized devices or address heart blockages.
However, here’s something to keep in mind – The aforementioned treatments are definitely something cardiologists adhere to. However, once a patient with heart attack reaches the emergency room, a medical team will be there to conduct diagnostic tests to identify the underlying cause of sudden heart problem. Accordingly, treatment strategies are tailored to address the specific causes and conditions.
Conclusion:

After delving deep into topics like – cardiac attacks and NDEs, you may be left pondering the question of how to prevent cardiac arrest. The answer lies in a proactive approach that combines lifestyle changes and prudent measures. Maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management is paramount, as is the management of underlying conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol levels.
Considering the rising cases of cardiac arrest in the US, it’s advisable to learn and practice CPR, a skill that can prove life-saving in emergencies. For those at a higher risk, the consideration of implantable devices like defibrillators is worth exploring. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers provide a crucial means of monitoring heart health, enabling early intervention and the adoption of personalized preventive measures. Furthermore, educating oneself about cardiac risk factors and promptly seeking medical attention for symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath are essential steps in the journey to preventing cardiac arrest.
Your proactive approach to heart health can be the key to a longer and healthier life!
References:
- Study of cardiac arrest survivors reveals insight into near-death experiences
Source: nbcnews.com - Cardiac Arrest
Source: cdc.gov - Near-Death Experiences and Psychotherapy
Source: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

MDForLives is a global healthcare intelligence platform where real-world perspectives are transformed into validated insights. We bring together diverse healthcare experiences to discover, share, and shape the future of healthcare through data-backed understanding.