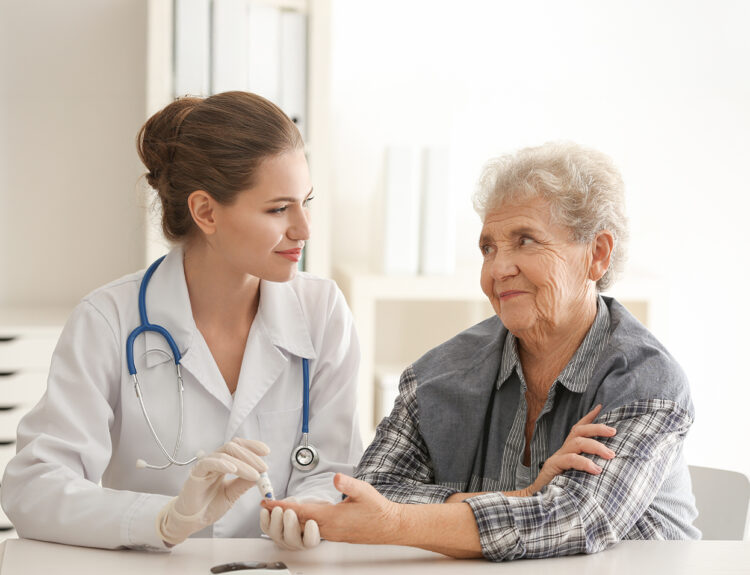
Living with diabetes can be a challenging journey. It requires constant vigilance, careful management of blood sugar levels, lifestyle adjustments and emotional resilience. However, individuals with diabetes don’t have to navigate this path alone. Patient support groups and community resources play a pivotal role in helping patients cope with the physical, emotional and psychological aspects of this chronic condition.
What is diabetes?
A chronic health condition that affects the conversion of food into energy is diabetes. Most of the food consumed is transformed into sugar (glucose) and is released into the bloodstream. When blood sugar levels rise, a signal is sent to the pancreas to release insulin, which functions as a key to allow the entry of blood sugar into the body’s cells for energy utilization. The pancreas is a vital organ located in the abdominal region, nestled behind the stomach. In the case of diabetes, either insufficient insulin is produced by the body or it is not utilized effectively. When there is an inadequate supply of insulin or the response of cells to insulin is diminished, excess blood sugar remains in the bloodstream. As a result, serious health issues, such as heart disease, vision impairment and kidney disease, can be caused by prolonged elevation of blood sugar levels.
There are three primary categories of diabetes: type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is believed to originate from an autoimmune response where the body mistakenly attacks itself, leading to the cessation of insulin production.
- Type 2 diabetes: Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body struggles to utilize insulin effectively, resulting in an inability to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
- Gestational diabetes: Gestational diabetes emerges during pregnancy in women who have not previously experienced diabetes.
The Diabetes Epidemic
To understand the importance of support groups and community resources for patients with diabetes, it’s crucial to grasp the scale of the diabetes epidemic. In 2021, approximately 537 million adults, which equates to 1 in 10 individuals, were dealing with diabetes. It is projected that this figure will increase to 643 million by 2030 and further rise to 783 million by 2045. Additionally, nearly half of all adults with diabetes, about 44%, go undiagnosed, totaling around 240 million people, with the majority of them having type 2 diabetes. Moreover, more than 75% of individuals with diabetes reside in low- and middle-income nations. Approximately 541 million adults are in a heightened state of risk for developing type 2 diabetes, while over 1.2 million children and adolescents (aged 0-19 years) are coping with type 1 diabetes. In 2021, diabetes led to 6.7 million fatalities.
The growing prevalence of diabetes highlights the need for comprehensive support systems that can address the unique challenges faced by individuals living with this condition.
The Emotional Impact of Diabetes
Receiving a diagnosis of diabetes is not just a medical event; it’s an emotional journey that can significantly affect an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. The emotional impact of diabetes is multifaceted and can encompass a wide spectrum of feelings, including fear, anxiety, frustration and even depression.
- Fear: When someone is diagnosed with diabetes, fear is often one of the initial emotions they experience. Fear of the unknown, fear of potential complications and fear of how diabetes will change their life can be overwhelming. Individuals may worry about the need for lifelong medication or insulin injections and how these will impact their daily routines.
- Anxiety: Living with diabetes can be anxiety-inducing due to the constant monitoring of blood sugar levels and the need to make crucial decisions about food, exercise and medication. Anxiety can arise from the uncertainty of how the body will respond to these decisions and the fear of experiencing hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) episodes.
- Frustration: Managing diabetes can be frustrating, particularly when blood sugar levels seem unpredictable or difficult to control. Individuals may become frustrated with themselves or the condition itself, especially if they feel they are doing everything right and still facing challenges in maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
- Depression: For some individuals, the emotional toll of diabetes can lead to clinical depression. Coping with a chronic condition that requires constant attention and lifestyle modifications can be mentally exhausting. Feelings of hopelessness, sadness and a sense of losing control over one’s life can contribute to depression.
- Isolation: Many diabetes patients may feel isolated in their journey. They might perceive themselves as different from their peers or family members who do not have diabetes, leading to a sense of loneliness. Social events, dietary restrictions and the need for regular blood sugar monitoring can sometimes create a barrier between individuals with diabetes and their social circles.
- Overwhelm: The demands of diabetes management, which often include medication or insulin administration, regular glucose monitoring, dietary adjustments and exercise regimens, can be overwhelming. Individuals may feel like they are juggling multiple responsibilities and worry about making mistakes that could have serious health consequences.
This emotional toll goes beyond the physical aspects of diabetes and can profoundly impact an individual’s overall well-being and quality of life. Recognizing and addressing these emotions is crucial for holistic diabetes care. Support systems, such as healthcare professionals, support groups and loved ones, can play a vital role in helping individuals navigate the emotional challenges of diabetes and develop effective coping strategies.
Benefits of Patient Support Groups
Support groups for diabetes patients provide a safe and nurturing environment for individuals to share their experiences, emotions and challenges. Here are some key benefits of participating in such groups:
- Emotional Support: Support groups offer a space where participants can express their feelings, fears and frustrations without judgment. Connecting with others who face similar challenges helps individuals feel understood and less alone.
- Shared Knowledge: Members of support groups often share diabetes patient care plans and valuable insights, tips and strategies for managing diabetes effectively. Learning from others’ experiences can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
- Motivation: Support groups can serve as a source of motivation and inspiration. Seeing others successfully manage their diabetes can instill hope and encourage individuals to stay committed to their own health goals.
- Improved Coping Skills: Through interactions with group members, individuals can develop better coping skills to handle the emotional and practical aspects of diabetes. This can lead to reduced stress and anxiety.
- Accountability: Being part of a support group creates a sense of accountability. Knowing that others are invested in their well-being can motivate individuals to stick to their diabetes management plans.
Community Resources for Patients with Diabetes
In addition to support groups, community resources are essential for diabetes patients. These resources encompass a wide range of services and initiatives that aim to improve diabetes education, access to care and overall quality of life. Here are some key community resources:
- Diabetes Education Programs: Community-based diabetes education programs offer valuable information on topics such as nutrition, exercise, medication management and blood glucose monitoring. These programs empower patients to make informed decisions about their health.
- Access to Healthcare Professionals: Community health clinics and centers often provide access to healthcare professionals specializing in diabetes care. This can be especially beneficial for individuals who may not have easy access to specialized medical care.
- Financial Assistance: Some community resources offer financial assistance or subsidies for diabetes-related expenses, including medications, glucose meters and testing supplies. This helps reduce the financial burden of managing diabetes.
- Fitness and Nutrition Classes: Many communities offer fitness and nutrition classes tailored to diabetes patients. These classes can help individuals adopt healthier lifestyles and manage their weight, a critical aspect of diabetes management.
- Advocacy and Awareness Campaigns: Community organizations and advocacy groups work to raise awareness about diabetes and advocate for policies that improve diabetes care and prevention. Their efforts can lead to positive changes on a broader scale.
The Holistic Approach to Diabetes Management
Combining the benefits of support groups and community resources creates a holistic approach to diabetes management. This approach acknowledges that diabetes affects not only physical health but also emotional and social well-being.
- Comprehensive Care: Diabetes support group online and community resources complement medical treatment by addressing the emotional and lifestyle aspects of diabetes. This holistic approach leads to better overall health outcomes.
- Peer-Led Initiatives: Some community resources involve peer-led initiatives where individuals who have successfully managed their diabetes take on mentorship roles. These mentors provide practical guidance and emotional support.
- Tailored Support: Patient support groups and community resources can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different populations, such as children with diabetes, teenagers, adults and seniors. This ensures that individuals receive relevant and age-appropriate support.

Conclusion:
In conclusion, the benefits of support groups and community resources for patients with diabetes cannot be overstated. These resources provide emotional support, shared knowledge, motivation and practical assistance that are vital for effectively managing this chronic condition. By embracing a holistic approach to diabetes management that includes both medical care and community support, individuals can lead healthier, happier lives despite the challenges of diabetes.
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, it is essential that we recognize the importance of diabetes support groups online and community resources in helping individuals navigate the complexities of living with diabetes. By fostering a sense of belonging, empowerment and shared knowledge, these resources empower diabetes patients to take control of their health and well-being. Together, we can work towards a future where diabetes is not just manageable but thriving with the support of a caring community.

MDForLives is a global healthcare intelligence platform where real-world perspectives are transformed into validated insights. We bring together diverse healthcare experiences to discover, share, and shape the future of healthcare through data-backed understanding.






